Saccoglossus is a genus of acorn worms belonging to the class Enteropneusta under the phylum Hemichordata. These worms live in shallow marine habitats, where they burrow through sandy or muddy substrates while feeding on organic particles. They play an important role in sediment turnover and nutrient recycling. Because Saccoglossus exhibits key hemichordate characteristics—such as the tripartite body plan of proboscis, collar, and trunk—it provides valuable insight into early deuterostome evolution and the origins of chordate anatomical features.
Classification of Saccoglossus
- Phylum :- Hemichordata (Marine, enterocoelous coelomate. Notochord confined to head region)
- Class :- Enteropneusta (Several gill-slits, intestine straight, solitary.)
- Family :- Harrimaniidae
- Genus :- Saccoglossus

Geographical distribution of Saccoglossus
It occurs in New Zealand, Australia, the Indo-Pacific region, the Atlantic coasts, and North America.
Habit and Habitat
It is marine, burrowing and tubicolous animal. These burrow in sand flats near low tide, line, living in semipermanent tunnels lined with mucous secretions. The mouth, which apparently cannot be closed, lies ventrally between the proboscis and collar. As the worm burrows much of the sand is swallowed.
Characteristics of Saccoglossus
- It is vermiform hemichordate.
- Body regionated into proboscis (prosoma) collar (mesosoma) and trunk. (metasoma).
- Proboscis is exceptionally longer than any other enteropneust.
- Collar slightly overhangs the beginning of trunk, covering three of four gill-slits. Trunk is differentiated into three regions. In the anterior part numerous pairs of gill-slits open externally near the mid-dorsal line.
- Middle part has gonads which are grey in female and yellow in male.
- Posterior region has only posterior part of intestine and tapers gradually to anus.
- Hepatic sacculations and genital ridges.
- So well developed in Balanoglossus, are absent.
- Synapticulae are absent in pharynx and such tongue bars hang freely in gill-slits. Its affinities etc., are similar to those of Balanoglossus.
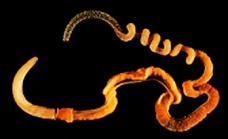
Identification
Since the specimen has long proboscis and all above features, hence it is Saccoglossus.