Crayfish vs Lobster : Differences Explained
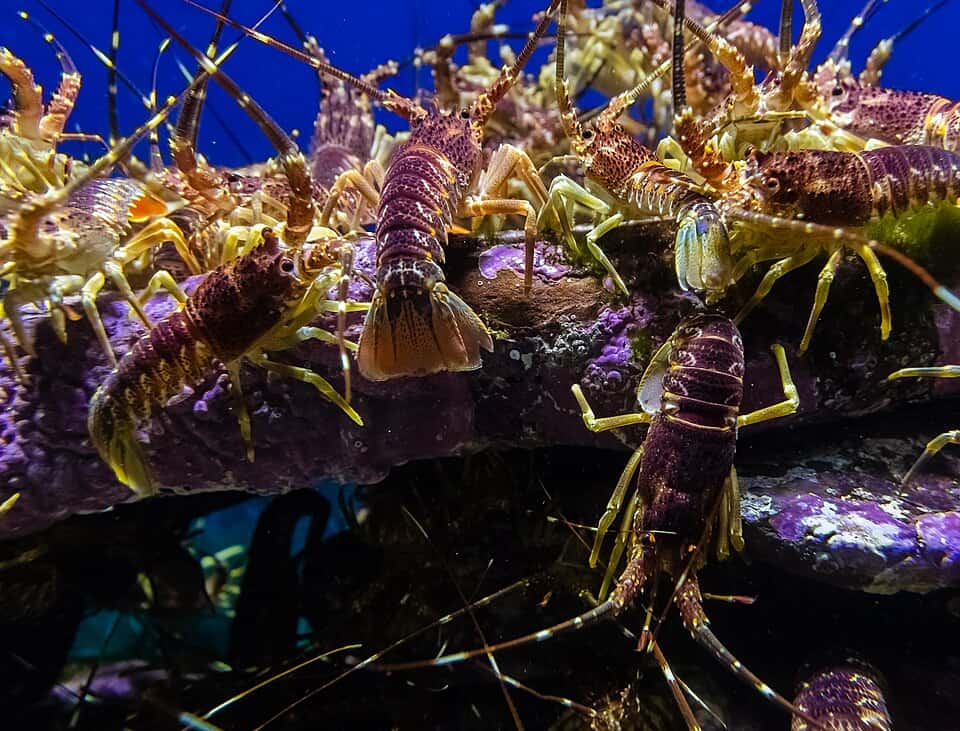
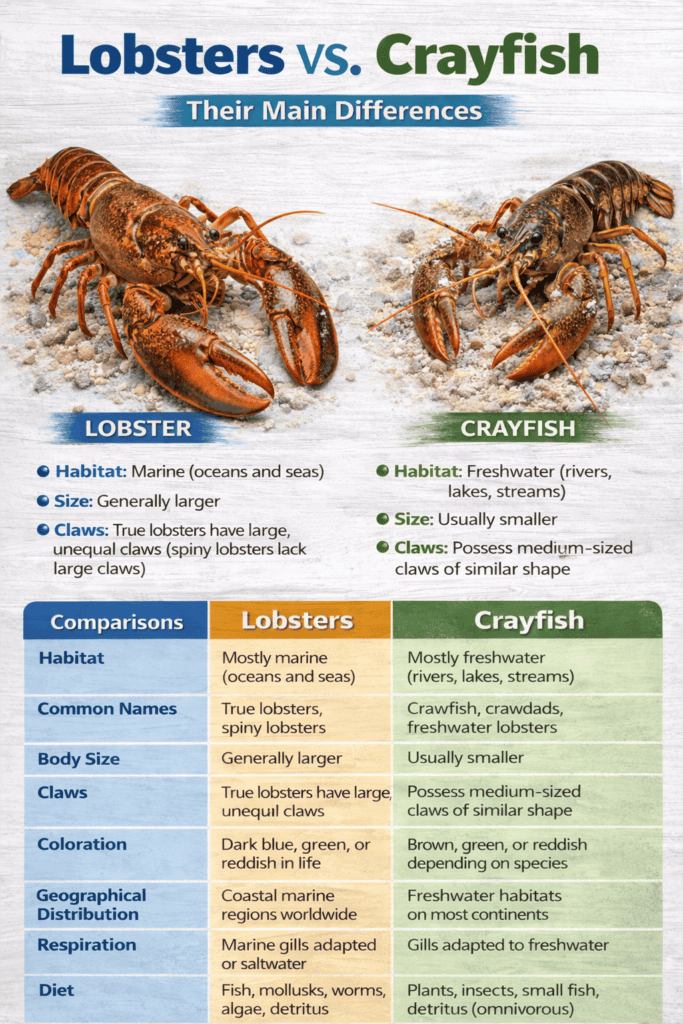
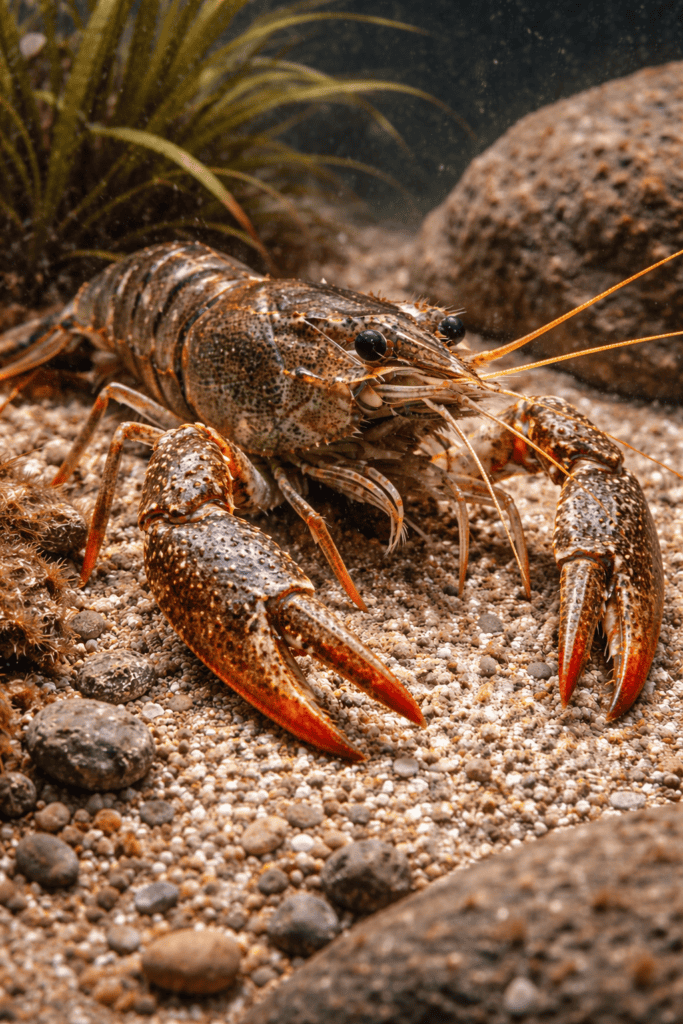
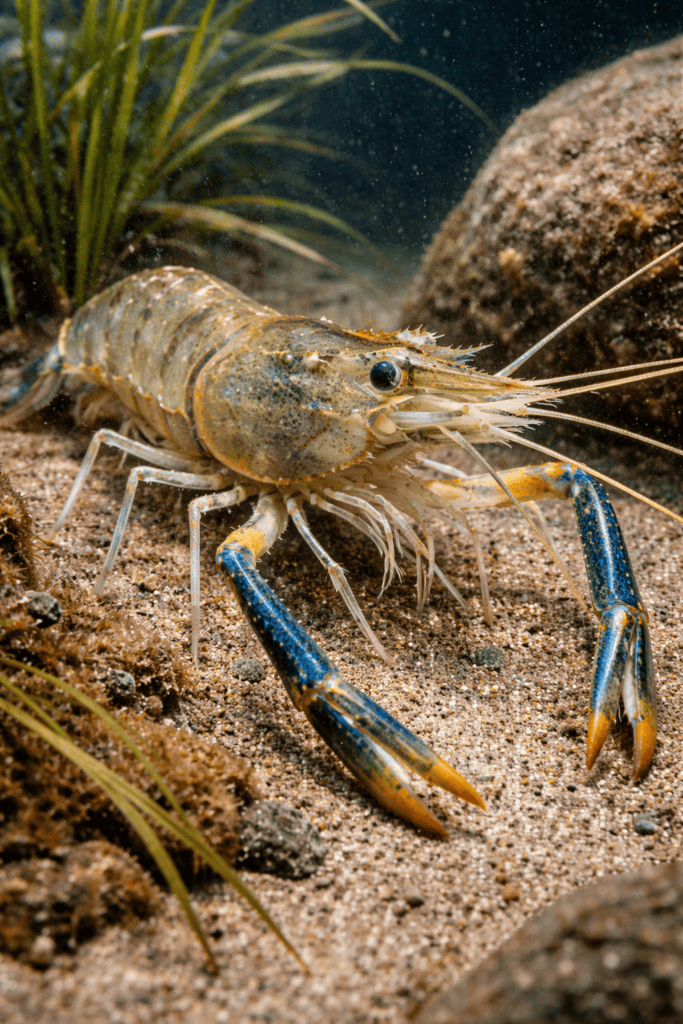
Crayfish vs Lobster : Differences Explained – The fact that lobsters are sometimes referred to as crayfish in some places only serves to further confuse the two species. They do appear strikingly same, so it’s simple to make the mistake. Both have big pincers and robust exoskeletons, and they both live in water. In actuality, however, they belong to two distinct species.