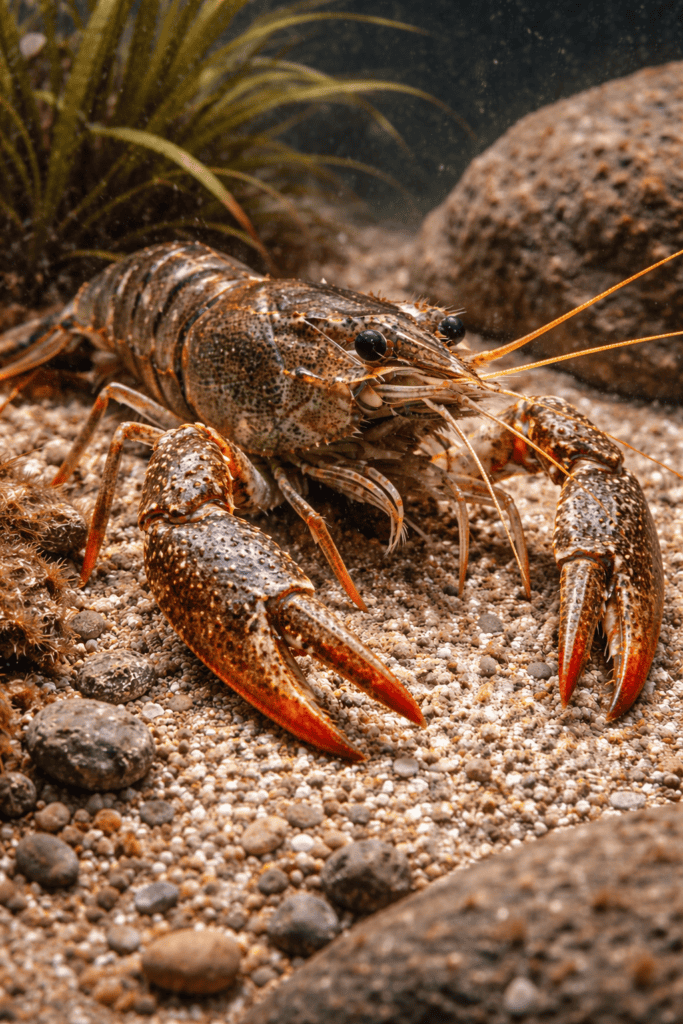
Astacus astacus (commonly known as the European crayfish, noble crayfish, or broad-legged crayfish) is a freshwater decapod native to Europe from France to Russia to Scandinavia. Commonly found in clear, unpolluted rivers and lakes, this nocturnal species (up to 16 cm) is a traditional food source, but is now listed as endangered due to habitat loss and crayfish epidemics.
Classification of Astacus astacus
| Taxonomic Rank | Name | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia | Multicellular eukaryotes |
| Phylum | Arthropoda | Segmented invertebrates with jointed appendages |
| Subphylum | Crustacea | Mostly aquatic arthropods with exoskeleton |
| Class | Malacostraca | Largest class of crustaceans with ten legs (decapods) |
| Order | Decapoda | Ten-legged crustaceans including shrimps and crabs |
| Suborder | Dendrobranchiata | Prawns with branched gills and distinct reproductive traits |
| Superfamily | Penaeoidea | Prawns with elongated bodies and well-developed rostra |
| Family | Penaeidae | Commercially important penaeid shrimps |
| Genus | Astacus | |
| Species | astacus |
Habit and habitat
Astacus is common in streams, rivers and lakes. It is omnivorous feeding on any alive or dead matter. Its acts as scavenger.
Distribution
It is found on the Pacific slope, Europe, Asia, England, U.S.A., Australia and New Zealand.
Comments on Astacus
- Commonly called as cray-fish.
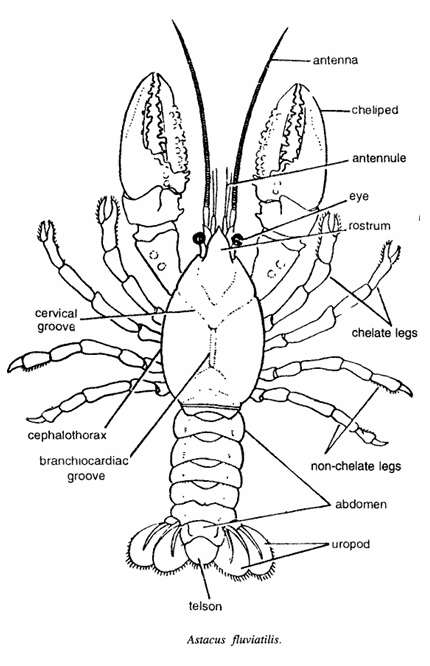
- Body is essentially sub-cylindrical in shape, small, about 9 cm in length and divided into anterior cephalothorax, middle flexible abdomen and posterior telson.
- Cephalothorax comprises of head and thorax and is covered by carapace, which is produced into short and unserrated rostrum and on sides covers the gills.
- Cervical groove demarcates head and thorax.
- Eyes are stalked, antennules short and antennae elongated. Appendages are 19 pairs-5 cephalic, 8 thoracic and 6 abdominal.
- Abdomen contains 6 pairs of swimming appendages or pleopods and a telson.
- Abdominal segments are movable upon one another in a vertical plane. The abdomen is long and extended and ending in tail fans.
- Walking legs are chelate. One pair of legs are called as chelipeds.
- These are much enlarged appendages, terminating in huge claws or chelate.
- Telson fonns a tail-fan together with uropods.
Special features of Astacus
Female carries hundreds of small, rounded eggs on the ventral side of her abdomen. Eggs hatch into young cray-fishes, which are exact replicas of the mother and cling to her for some time.
Economic value
It is relished as food.
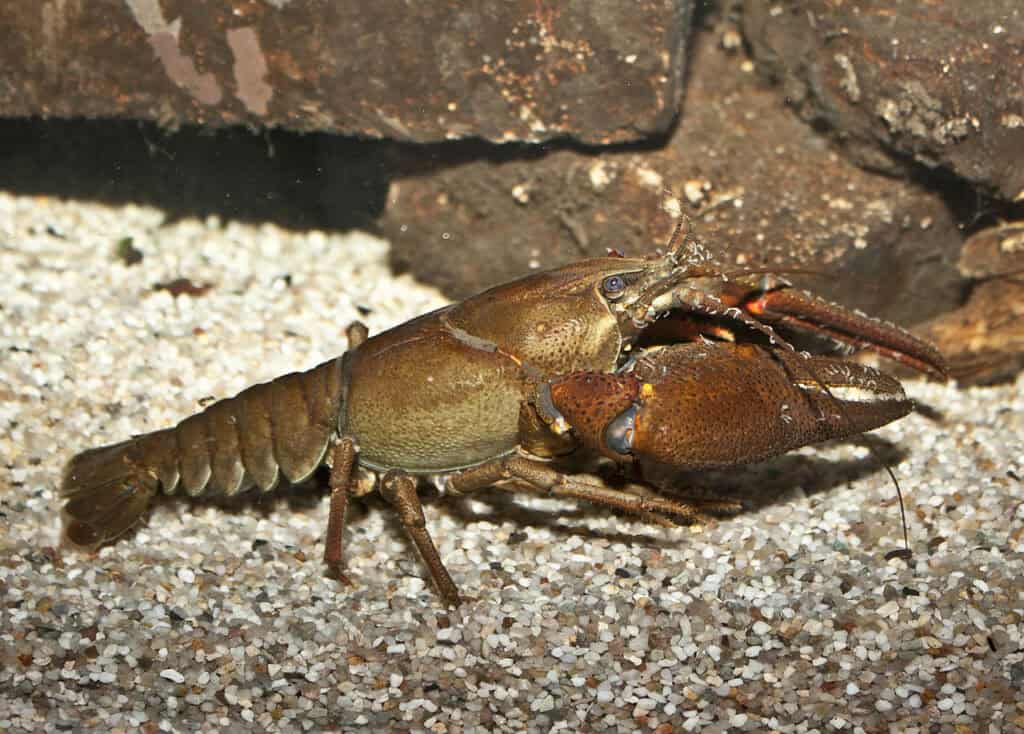

Identification
Since the specimen contains, cephalothorax, cheliped, fan-like uropod and all above features hence it is Astacus.
See other posts also