The Atlantic horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus) is the only member of the genus Limulus that is still alive. Although several other species have been identified and subsequently assigned to other genera, the genus now has one fossil species credited to it.
Classification of Limulus (Horseshoe crab)
| Phylum | Arthropoda | Jointed appendages. |
| Class | Arachnida | Terrestrial or aquatic arthropods with book-lungs or trachea and without antennae, mandibles and jaws. |
| Order | Xiphosura | Delobranchiate in which carapace is covered by horseshoe shaped carapace. |
| Genus | limulus | Horseshoe crab |

Habit and habitat
Limulus is marine found in muddy bottom, 2 to 6 fathoms deep, partly buried and crawling in sand for food. The Horseshoe crab lives in shallow water along the shore, where it burrows in the sand and mud and eats worms and small animals. It comes to sandy beaches in the early summer to breed
Distribution
It inhabits eastern coast of Asia and its island and eastern cost of North American from Nova Scotia to Florida. It has restricted and discontinuous distribution.
Comments on Limulus (Horseshoe crab)
- Commonly called as Horseshoe crab.
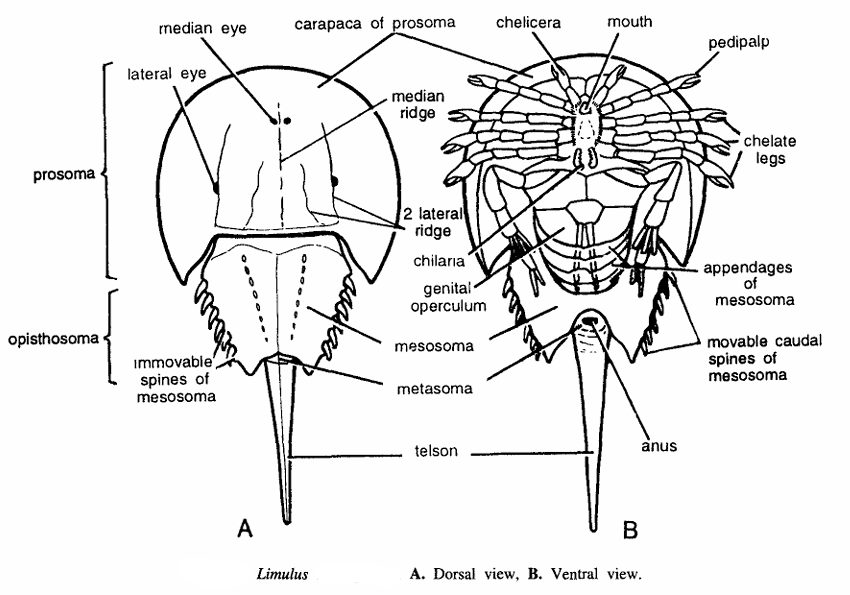
- Body is differentiated into a broad horseshoe-shaped prosoma and a small nearly triangular opisthosoma.
- Body regions are cephalothorax, abdomen and a long spike like telson or tail.
- Prosoma is convex above with sloping sides. It contains one median and two lateral longitudinal ridges.
- Prosoma is covered by a large semicircular carapace and joined to opisthosoma by a broad hinge.
- The prosomatic appendages are ftrst pair of chelate chelicerae, while 2 to 7 segments bear a pair of chelate walking legs each.
- Carapace also bears one pair of median and two large composite sub-dorsal or lateral eyes.
- Opisthosoma comprises of six segments, the mesosoma, a vestigial metasoma and a long spine like telson.
- Mesosoma contains 6 pairs of immovable spines. Chelicerae are 3-jointed small and chelate.
- Legs are biramous and the last pair are not paddle-shaped. First pair of mesosomatic appendages form the genital operculum.
- Opisthosoma has book gills. The post anal caudal spine is hinged and freely movable. Young are planktonic larvae (Trilobite stage).
Special features
Limulus has majestic look and hence it is called as Horseshoe crab. Limulus has been reported from Paleozoic period when it was abundant and only five species of it, known since Triassic period, are living today, so it has long fossil history. The Horseshoe crab although of large size, have little economic importance. Sometimes they are fed to chicken and pigs.
Identification
Since the specimen contains semicircular carapace and all above features, hence it is Horseshoe crab.
See other Posts also
- SKATE FISH
- The Coolest Deep-Sea Animals
- Fan-Throated Lizard (Sitana ponticeriana)
- Sailfish The Fastest Fish in the Ocean
- MELURSUS URSINUS (SLOTH BEAR)