The predatory arachnids known as scorpions (Palamnaeus) have eight legs, two grabbing pincers, and a slender, segmented tail that always ends with a stinger and is frequently carried in a distinctive forward curve over the back. Scorpions have a 435 million-year evolutionary history. They are found on every continent except Antarctica and primarily inhabit deserts, but they have adapted to a variety of climatic situations. There are now 22 extant (alive) families identified out of over 2,500 documented species. In light of genomic research conducted in the twenty-first century, their classification is being updated.

Classification of Palamnaeus (Scorpion)
| Phylum | Arthropoda | Jointed appendages |
| Sub-phylum | Chelicerata | Chelicerata split from Mandibulata by the mid-Cambrian |
| Class | Arachnida | Terrestrial or aquatic arthropods with book-lungs or trachea and without antennae, mandibles and jaws. |
| Order | Scorpiones | Embolobranchiates in which the prosoma bealS 3-jointed chelicerae and chelate pedipals. |
| Genus | Palamnaeus | Scorpion |
Habit and habitat
Palamnaeus is a nocturnal arthropod, found in sand, crevices and under stones and in bark of dead trees. It feeds on insects and spiders which they often kill with the sting.
Distribution
It has cosmopolitan distribution and specially found in India, Europe and U.S.A.
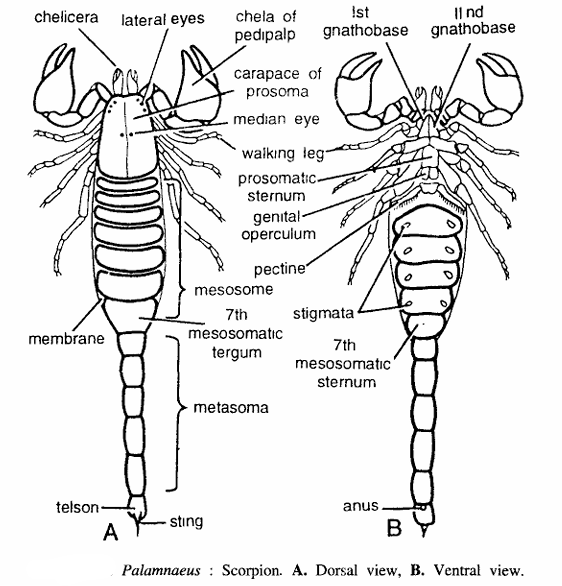
Comments on Palamnaeus (Scorpion)
- Commonly called as scorpion.
- Body is elongated, segmented and differentiated into anterior prosoma and posterior opisthosoma.
- Opisthosoma is sub-divided into a broad anterior mesosoma and a narrow posterior metasoma.
- Prosoma is covered dorsally by a carapace and its appendages are a pair of small chelate chelicerae, a pair of large chelate pedipalps, 4 pairs of walking legs and several ocelli.
- Body is encased in chitinous covering. The dorsal side covering is called as tergum, side one pleuron and ventral one sternum.
- Mesosoma is composed of 7 broad segments and metasoma of 5 narrow segments.
- Last metasomatic segment is telson containing a sting. Ventrally the sternum of first mesosomatic segment contains a pair of genital openings.
- The second meso somatic sternum bears a pair of sensory pectines, while third, fourth, fifth and sixth mesosomatic segments contain 4 pairs of bilateral stigmata, which are the openings of the respiratory booklungs.
- Metasoma is limbless. Just beneath chelicerae there are I and II gnathobases.
- Sexes are separate but without sexual dimorphism. Viviparous.

Special features
Scorpions are harmful to mankind; its sting causes extreme pain. fever and in some cases collapse. The sting has a poison duct from the sting gland present in telson. Other common forms are Buthus and Centrurus.
Identification
Since specimen has prosoma, mesosoma, metasoma and all above features, hence it is Scorpion.
See other Posts also
- RHINOCEROS
- PECTORAL GIRDLEs IN VERTEBRATES
- HERDMANIA SLIDES
- Frogfish Facts, Species, Behavior, Reproduction
- CHIMAERA (RAT FISH)