Ophiothrix: An In-Depth Overview of Morphology, Classification, Habitat, Behavior, Reproduction, and Ecological Significance
Ophiothrix is a large and diverse genus of brittle stars within the family Ophiotrichidae, belonging to the class Ophiuroidea and phylum Echinodermata. With approximately 93 recognized species, Ophiothrix is one of the most widespread brittle star genera, occupying diverse marine habitats worldwide, from tropical coral reefs to deep-water ecosystems, even reaching Arctic and Antarctic waters. Noted for their slender and flexible arms adorned with spines, many Ophiothrix species display vibrant colors and complex behaviors that contribute to their ecological roles. These brittle stars are significant benthic organisms contributing to nutrient cycling, habitat complexity, and reef biodiversity.
Classification of Ophiothrix
| Taxonomic Rank | Name | Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia | Multicellular, heterotrophic marine animals |
| Phylum | Echinodermata | Marine invertebrates with radially symmetric calcareous skeletons |
| Class | Ophiuroidea | Brittle stars characterized by a distinct central disc and flexible arms |
| Order | Ophiurida | Diverse brittle stars with jointed arms |
| Family | Ophiotrichidae | Brittle stars with scaly and spiny arms |
| Genus | Ophiothrix | Agile and often colorful brittle stars with spiny arms |
Habitat and Habit
Ophiothrix brittle stars exhibit remarkable ecological plasticity, thriving in shallow coastal waters, coral reefs, rocky habitats, and soft sedimentary bottoms. Many species are nocturnal, spending daylight hours hidden under rocks, among coral branches, or in crevices to avoid predation, while engaging in active foraging at night. Their movement is characterized by rapid and agile arm motions, enabling efficient locomotion, escape, and prey capture over the seabed surface.
This genus often associates closely with coral and sponge habitats, contributing to reef complexity and functioning as scavengers and filter feeders. Some species have been observed occupying habitats extending down to depths of around 350 meters, while others remain in intertidal zones.
Geographical Distribution
Ophiothrix has a cosmopolitan distribution, reported from tropical, subtropical, and even polar marine regions. It is widely found in the Indo-Pacific region, Western Atlantic, Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, and parts of Europe. Specific species like Ophiothrix fragilis have localized populations in the North Sea and the Atlantic coasts of Europe and Africa, while others have adapted to Caribbean and Pacific reefs.
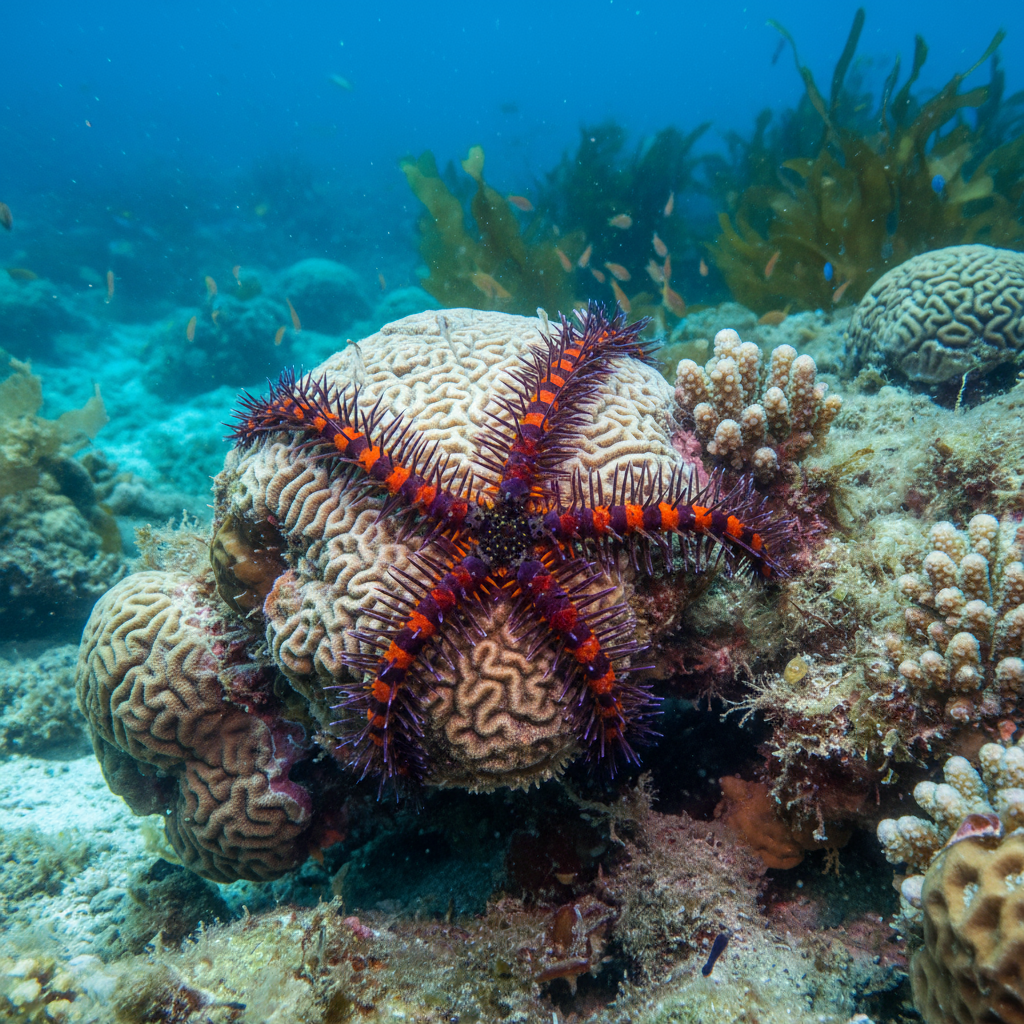

General Characteristics
The genus exhibits several defining morphological traits:
- Commonly called as Brittle star.
- Ophiothrix reveals considerable variation in spine armature and colour pattern.
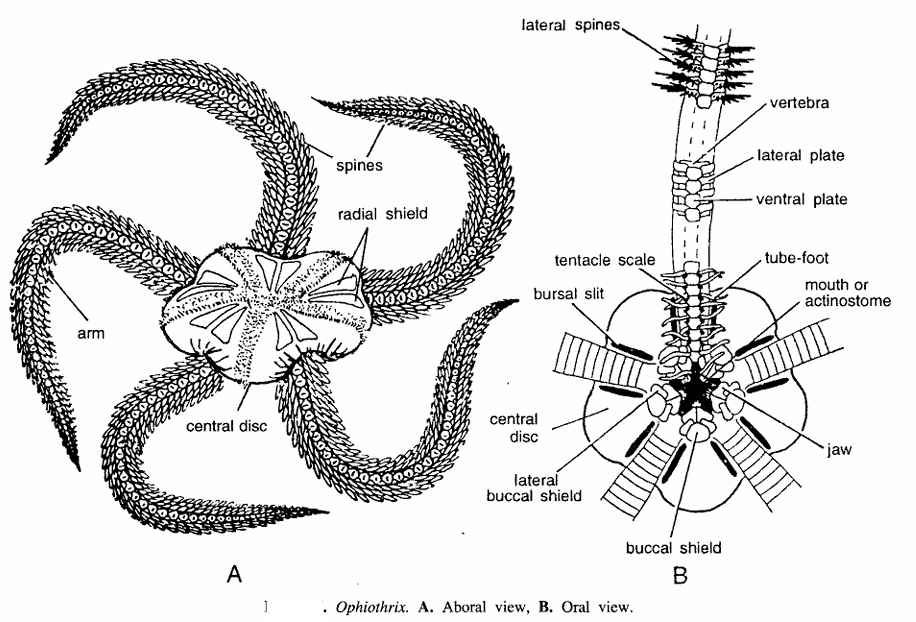
- No two individuals are alike. Body divisible into oral and aboral surfaces.
- Central disc and arms quite distinct. Spines on the disc continue round its sites, lateral spines are larger in size.
- Interradially and on edges of oral surfaces. Aboral surface has radial shields in central disc.
- Mouth in oral surface has complicated system of plates, spines and tube feet. Inter-radially buccal shields are present and beneath on lateral position are lateral buccal shield.
- Around mouth are jaw. At the base of each arm are slit like Bursal slit.
- Oral surface reveals each arm is made up of vertebral consisting of lateral plates and ventral plate.
- Lateral spines, tube foot, jaw and tentacle scale are seen. Aboral surface contains dorsal plates.
- A pentagonal central disc typically covered with small granules, scales, or plates, sometimes colored vividly.
- Five slender, long, tapering arms distinctly separated from the central disc.
- Arms possess alternating spines and scales, enabling tactile and protective functions.
- Mouth located subcentrally on the ventral disc, surrounded by jaws with denticles aiding in food processing.
- Tube feet are generally small and function more in sensory roles than locomotion.
- Coloration is highly variable across species, ranging from pale shades to brilliant hues of orange, red, purple, and yellow, often patterned for camouflage or display.
Special Features
Ophiothrix species are notable for their spiny arm morphology, which helps deter predators while enhancing surface area for sensory reception. Their ability to autotomize arms and regenerate them is a key defense mechanism allowing survival against predation or injury.
Many species in Ophiothrix exhibit vibrant and variable coloration that aids in cryptic camouflage or aposematic signaling. Some species have demonstrated unique reproductive and developmental physiology, including seasonal spawning behaviors and planktonic larval stages.
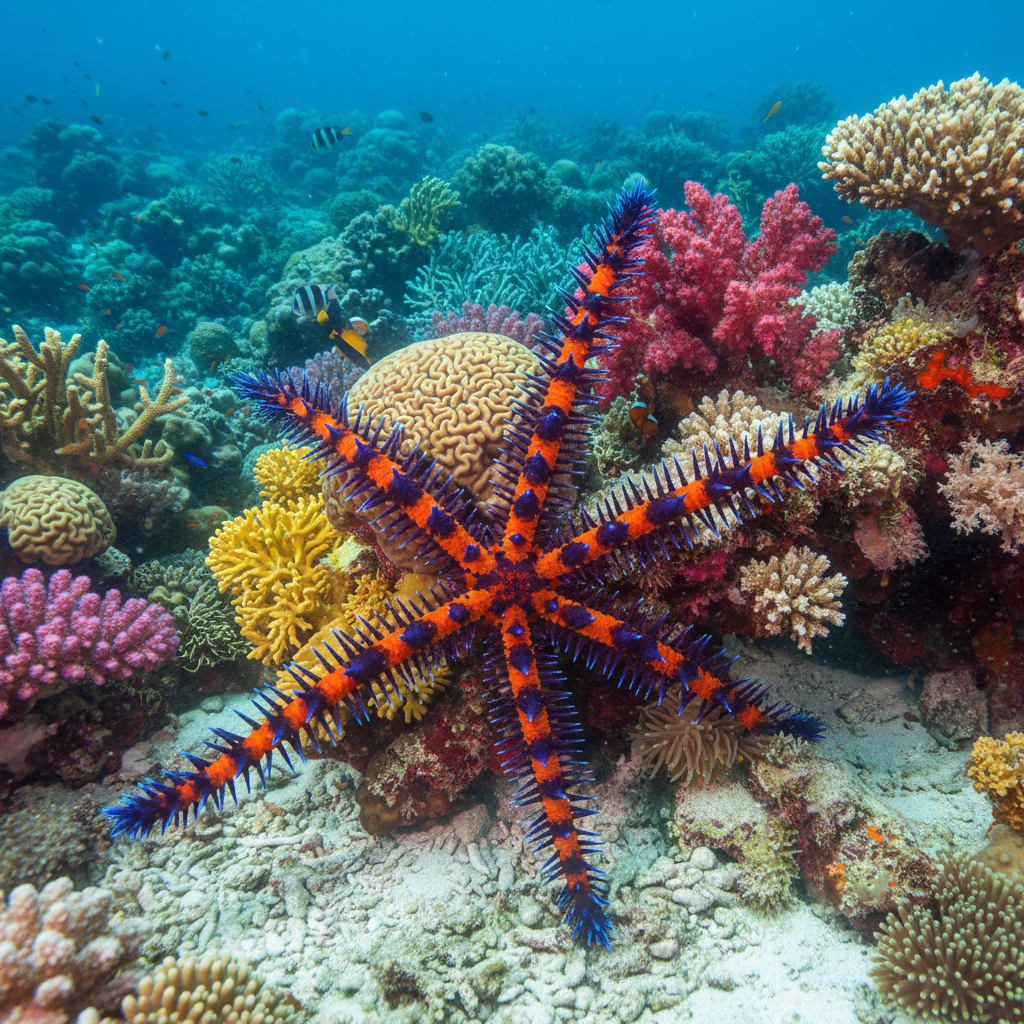

Behavior and Feeding
These brittle stars are opportunistic feeders, using their spiny arms and tube feet to gather detritus, plankton, and small invertebrates. They display both scavenging and suspension feeding behaviors, sometimes elevating arms into the water column to collect passing food particles.
Their locomotion involves coordinated wriggling and pulling with their flexible arms, often enabling rapid escape from threats. Nocturnal activity is typical, enhancing feeding efficiency and reducing exposure to daytime predators.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Ophiothrix species reproduce sexually via external fertilization. During spawning seasons, adults release gametes into the water, where fertilization occurs externally. The resulting larvae, called ophiopluteus, undergo several planktonic developmental stages before settling on the seabed and metamorphosing into juvenile brittle stars.
Life span ranges from several years, with reproduction often seasonal but sometimes continuous depending on habitat and environmental conditions. Juvenile morphology resembles adults, with progressive arm and disc development.
Ecological Importance
Ophiothrix brittle stars occupy essential ecological niches in marine ecosystems. By scavenging and predating on small organisms, they help regulate benthic community structure and recycle nutrients. Their activities contribute to bioturbation, which enhances sediment oxygenation and promotes habitat heterogeneity.
Moreover, due to their sensitivity to environmental changes, Ophiothrix species serve as bioindicators for coral reef health and water quality. Their abundance and diversity also indicate ecosystem biodiversity and resilience.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ophiothrix
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3689063/
- https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Ophiothrix_fragilis/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0967063716304320
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ophiothrix_fragilis
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10358340/
- https://www.cmlre.gov.in/sites/default/files/uploadfiles/Usha_Brittle%20stars_SEAS_catalogue_compressed%20(1).pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ece3.70284
- https://www.ebsco.com/research-starters/science/common-brittle-star
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.