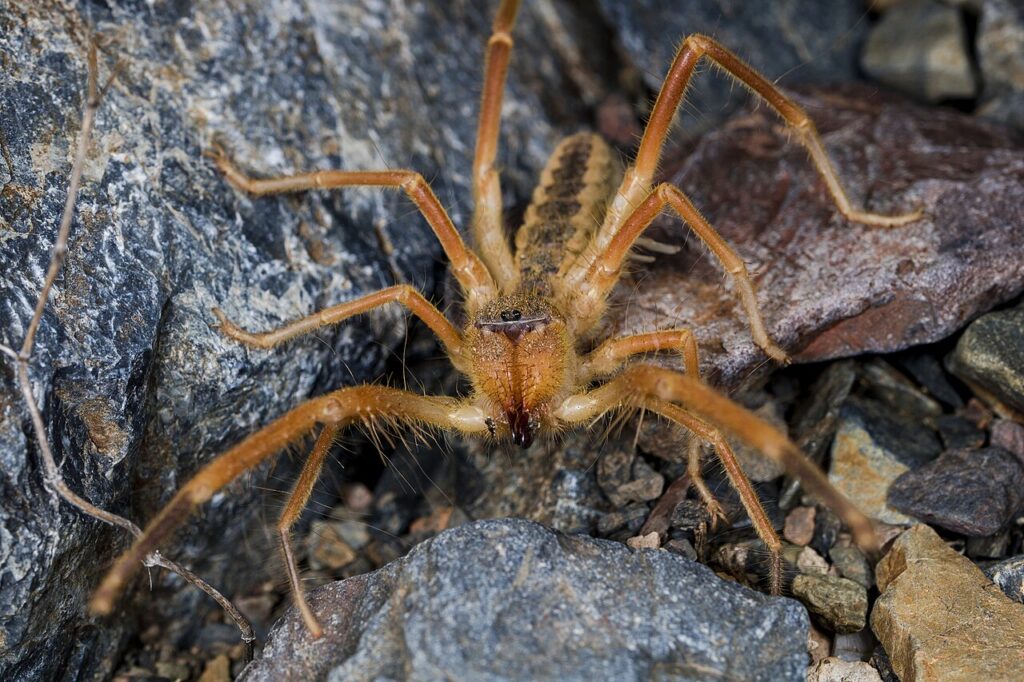
Solifuges, or sun spiders, belong to the genus Galeodes. This genus has around 200 species that are distributed throughout Asia, southeastern Europe, and northern Africa. They are mostly nocturnal and found in dry environments, just like other solifuges. They are not as robust or as dark and contrastingly colored as some other solifuges, and they frequently have lengthy hairy appendages. Certain species of Galeodes can make noises through stridulation. These have a protective purpose and are typically raspy or hiss-like, possibly mimicking the noises of vipers.[1] Similar to other solifuges, the male uses their chelicera to maneuver a spermatogonia into the female vaginal opening during mating. The male approaches the female by stroking her with his palps.

Classification of Galeodes
| Phylum | Arthropoda | Jointed appendages. |
| Class | Arachnida | Terrestrial or aquatic arthropods with book-lungs or trachea and without antennae, mandibles and jaws. |
| Order | Solifugae | Carapace of prosoma divided. |
| Genus | Galeodes |
Habit and habitat
Galeodes inhabits dry warm region.
Distribution
Found in India and Asia.
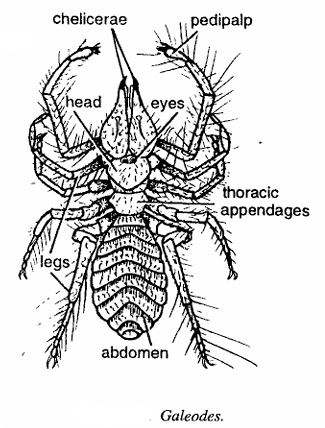
Comments on Galeodes
- Animal looks like Spider.
- Carapace of prosoma is divided with two chelicerae having two joins.
- The prosoma divided into head and thorax.
- Pedipalps are elongated, 6 jointed, leg like and sensory.
- Opisthosoma contains 10 segments.
- The thoracic appendages 3 pairs.
- The body of the animal has large number of setae.
Identification
Since the specimen has 6 joined pedipalp and all above characters, hence it is Galeodes.
See other posts also
- RHINOCEROS
- GECKO (WALL LIZARD)
- Differences between Crocodile vs Alligator vs Gharial
- What is Taxonomic Hierarchy?
- Crayfish vs Lobster : Differences Explained