Introduction
Loligo is a well-known genus of squid belonging to the family Loliginidae. These squids are admired for their speed, intelligence, and streamlined bodies. Because of their advanced adaptations and global distribution, species are significant not only in marine ecosystems but also in scientific research and international fisheries. This detailed article explores their morphology, ecological role, life cycle, and importance from both biological and human perspectives.
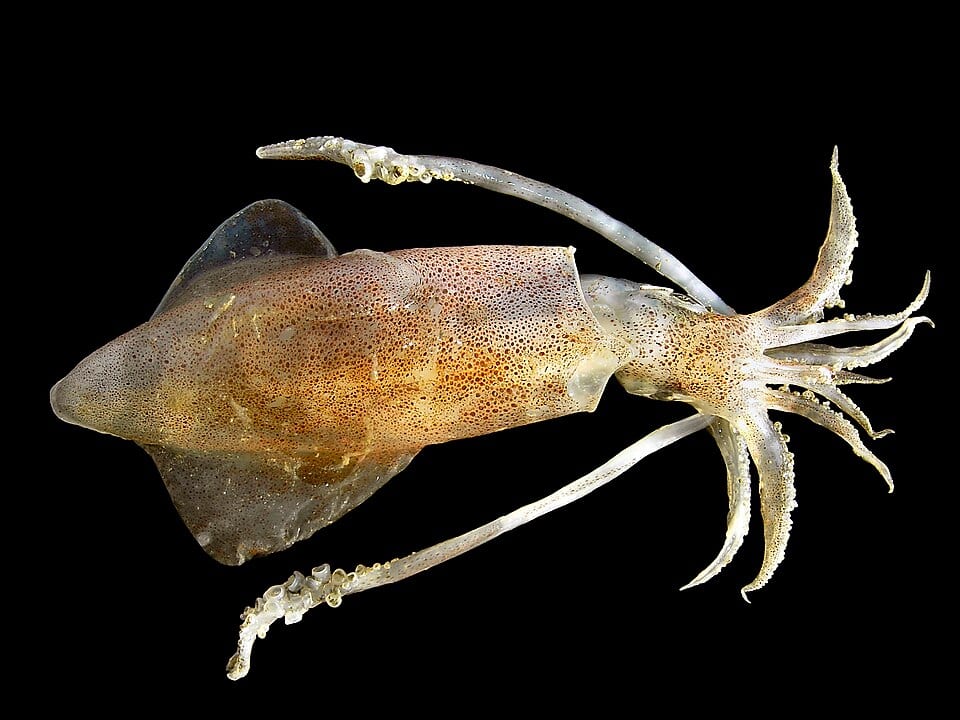

Classification of Loligo
| Taxonomic Rank | Classification | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia | Multicellular, heterotrophic organisms |
| Phylum | Mollusca | Soft-bodied invertebrates, often with shells |
| Class | Cephalopoda | Highly intelligent, tentacled marine animals |
| Order | Myopsida | Squids with covered eyes and coastal distribution |
| Family | Loliginidae | Long-bodied squids with well-developed fins |
| Genus | Loligo | Known for speed, agility, and advanced behavior |
Meaning and Origin of the Name
The name Loligo comes from classical Latin and was traditionally used to describe long-bodied squids. Over time, anatomists and zoologists adopted the term to represent a scientifically defined genus. Today, Loligo stands as one of the most studied squid groups, particularly for its smooth swimming style and elongated mantle, which resemble a pencil—hence the nickname “pencil squid.”
General Characteristics of Loligo
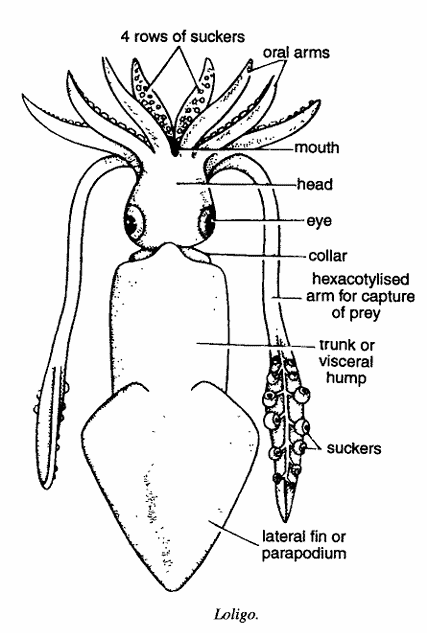
- Commonly called as squid.
- Body is fleshy, dorsoventrally flattened and differentiated into 3 regions
- anterior head containing 10 oral arms and a pair of eyes with olfactory crest
- middle trunk or visceral hump
- Posterior region with lateral fins or parapodia.
- Parapodium is contention of mantle. Head and trunk region are separated by collar.
- Each one of 8 oral arms contain four rows of pedicellate suckers ventrally.
- Remaining 2 oral arms on each side contains six pairs of pedicellate suckers.
- These arms are used for capturing prey and are calted as hectocotylised arms.
- In males one such arm is also modified as copulatory organ. Oral arm are modifications of the foot.
- After dissecting the animal, 2 ctenidia, 2 kidneys and 2 auricles are seen.
- Shell, internal horny and non-chambered and is used in maintenance of natural buoyancy.
- Ventral siphon is formed by the modification of foot. Sexes separate.
- Eggs are deposited in long cylin(l~”‘ql jelly masses
Species belonging to the genus Loligo possess several distinguishing features that set them apart from other squids.
1. Body Structure
Loligo squids have elongated, cylindrical mantles. Their lateral fins typically extend a significant length along the mantle, providing excellent stability and maneuverability. This fin design also allows smooth gliding through the water, contributing to their graceful movement patterns.
2. Arms and Tentacles
Loligo has eight arms and two tentacles. The tentacles are longer, ending in club-like structures equipped with rows of suckers. These specialized suckers help grasp prey securely, making hunting highly efficient.
3. Complex Eyes
The eyes of Loligo function similarly to vertebrate eyes. They offer depth perception and acute sensitivity to light, allowing Loligo to detect fast-moving predators or prey even in dim environments.
4. Chromatophores
Loligo possesses chromatophores—pigment-filled sacs in the skin that expand or contract to change color. This ability supports communication, camouflage, and predator avoidance.
5. Jet Propulsion
By forcing water through their muscular siphon, Loligo squids achieve rapid bursts of speed. This method of locomotion enables them to escape predators instantly.
Habitat and Distribution
Loligo species inhabit coastal waters in tropical and temperate regions worldwide. They often prefer:
- Continental shelves
- Sandy and muddy bottoms
- Bays and estuaries
- Shallow, well-oxygenated environments
Some species move offshore during breeding periods. Additionally, They tends to form schools, especially during migration and feeding.
Feeding Behavior
squids are active carnivorous predators. Their primary diet includes:
- Small fish
- Shrimps and other crustaceans
- Polychaete worms
- Small cephalopods
Their tentacles shoot forward rapidly to seize prey, and once captured, the prey is held by the arms while the sharp beak tears it into smaller pieces. Because of their speed and precision, Loligo squids are extremely effective hunters.
Defense Mechanisms
Loligo squids have evolved impressive strategies for avoiding predators.
Ink Release
When threatened, they release a dense cloud of ink that confuses predators and provides an opportunity to escape.
Camouflage
Their chromatophores allow them to blend perfectly with sandy substrates or open water, depending on their surroundings.
Rapid Evacuation
Jet propulsion enables sudden, high-speed escape responses.
Together, these strategies make Loligo exceptionally difficult prey.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Loligo squids have relatively short lifespans, often living one to two years, yet they reproduce prolifically.
Mating Behavior
During breeding seasons, huge aggregations form in shallow waters. Males display rapid color changes and fin movements to attract females. Competition among males is common and can be intense.
Egg Capsules
Females lay long, finger-like egg capsules, often referred to as “sea mops,” which they attach to seaweed, rocks, or the ocean floor. Each capsule contains multiple embryos.
Hatching and Early Growth
Juveniles emerge as miniature versions of adults and begin hunting soon after hatching. Their growth rate is extremely fast because of their high metabolism.

Ecological Importance of Loligo
Loligo squids play a crucial role in marine ecosystems.
- They regulate populations of small fish and crustaceans.
- They serve as prey for dolphins, seals, sharks, tunas, and seabirds.
- They contribute to nutrient cycling within coastal ecosystems.
Because they grow quickly and reproduce rapidly, Loligo squids help maintain ecological balance and energy flow in ocean environments.
Role in Human Society
They Loligo squids are economically valuable, contributing significantly to global seafood markets. They are harvested for:
- Food industries
- Fishing bait
- International export markets
Their mild flavor and soft texture make them popular in many cuisines.
Scientific Importance of Loligo
Loligo has made pivotal contributions to neuroscience. The giant axon of L. pealeii enabled scientists to understand nerve conduction, a discovery that led to major advancements in modern neurobiology.
Notable Species of Loligo
Some widely known species include:
- L. vulgaris – European squid
- L. pealeii – Longfin inshore squid
- L. forbesii – Veined squid
- L. opalescens – California market squid
Each species exhibits variations in size, distribution, and behavior, yet all share the defining Loligo characteristics.
Conclusion
The genus Loligo stands out as one of the most fascinating and ecologically important groups of squids. Their intelligence, speed, camouflage abilities, and advanced sensory systems illustrate the evolutionary success of cephalopods. Moreover, their invaluable role in research and contributions to global fisheries make Loligo essential to both science and society. Understanding their biology and habitat supports conservation efforts and sustainable management of marine resources.
References
- Marine Species Database – Loligo Overview
https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138380 - Animal Diversity Web – Loligo pealeii
https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Loligo_pealeii/ - FAO Fisheries – Cephalopod Species Catalogue
https://www.fao.org/3/ac481e/ac481e00.htm - Smithsonian Ocean Portal – Squid Biology
https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/invertebrates/squid - Encyclopedia of Life – Loligo Species
https://eol.org/pages/46428 - Journal of Cephalopod Biology – Research Articles
https://www.cephalopodresearch.org/journal/