Psittacula eupatria, commonly known as the Alexandrine Parakeet, is one of the largest and most striking parakeets of South and Southeast Asia. Recognized by its long tail, powerful red beak, and the characteristic maroon shoulder patch, the species thrives in forests, farmlands, and urban green spaces. Highly intelligent and social, Alexandrine Parakeets form strong pair bonds and communicate with loud, resonant calls. Their adaptability, vibrant coloration, and long history in aviculture make them one of the most familiar parrots across the Indian subcontinent.
Classification of Psittacula eupatria
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Aves (Biped and feathered vertebrates.)
- Sub Class :- Neornithes (True birds. Metacarpals fused.)
- Super Order :- Neognathae (Modern birds. no teeth. sternum keeled.)
- Order :- Psittaciformes
- Genus :- Psittacula
- Species :- euparia
Geographical distribution
Psittacula euparia is found in India, Pakistan, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and the United States. Eocene to Recent.
Habit and habitat
It is found on tall trees in flocks in city as well as in villages. It is also commonly found in the fruit trees, ripe crops and in jungles. Gregarious with loud voices. Feeds on fruits and crops.

General Characteristics of Psittacula eupatria
- Commonly called as Indian parakeet or parrot.
- It has brilliant blue-green plumage with massive, deeply-hooked red bill and a distinct maroon patch on each shoulder. P. krameri has no shoulder patches, while P. cyanocephala has a bluish-red head and maroon shoulder patches.
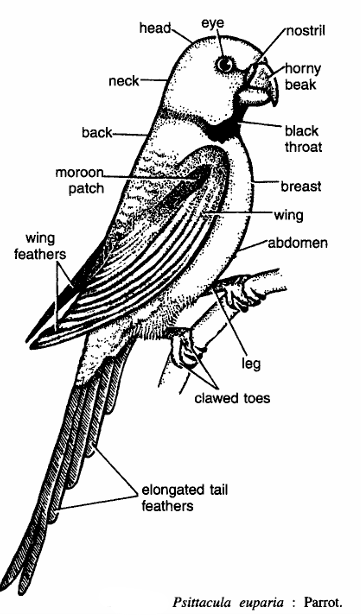
- Body is divisible into head, neck, back, breast and abdomen. Head contains eye, nostril and horny beaks.
- Beak stout, narrow, sharp edged and hooked at the tip and adapted for fruit eating.
- The upper mandible moves on the frontal bone of the skull, and its articulation causes the upper beak to rise automatically when the lower beak drops. The upper beak curves at the tip.
- The feet adapt for grasping, holding, and climbing. They show a zygodactylous arrangement in which digits I and IV point backward and digits II and III point forward, providing a firm grip on tree branches.
- Tail feathers elongated. Maroon patches on wing feathers. Flight is graceful and voice powerful.
- Female is green all over, but the male has a rose pink and black neck collar ring.
- Nesting season December to April.
Special Features of Psittacula eupatria
Parrot is a popular domesticated cage bird, found almost in every home and it copies and speaks some words like man. A serious agricultural pest to the cultivators and food growers. It causes enormous harm to standing crops and ripening orchard fruits. It eats maize, pulse, groundnuts and sometimes does considerable damage in newly sown fields. Its voice is sharp, well familiar and screaming kee-ak, kee-ak, kee-ak, kee-ak.
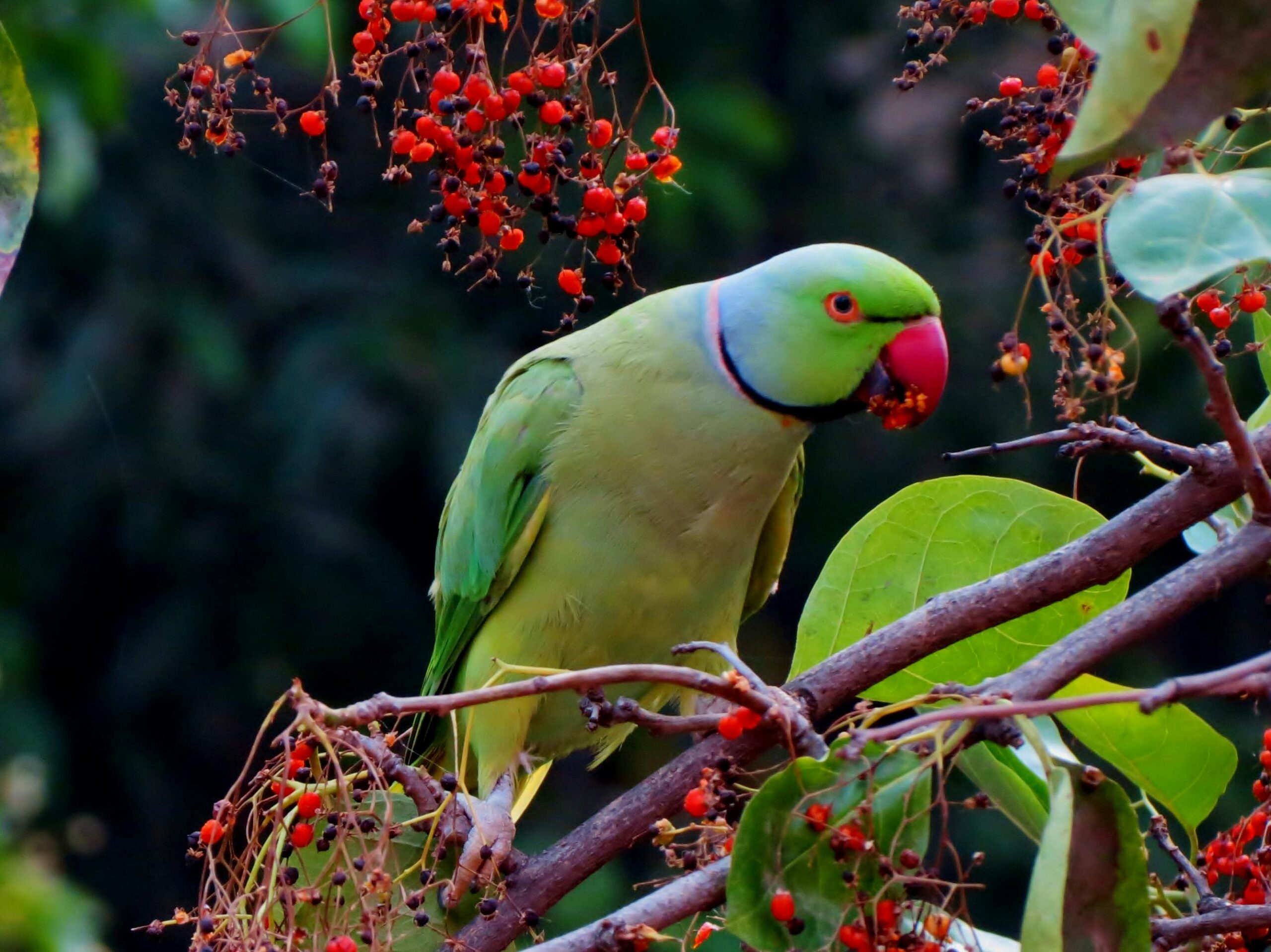

Identification
Since this bird has green plumage and all above features, hence it is Psittacula