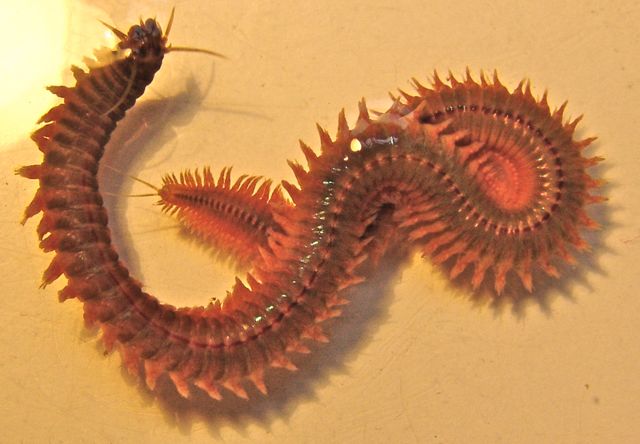
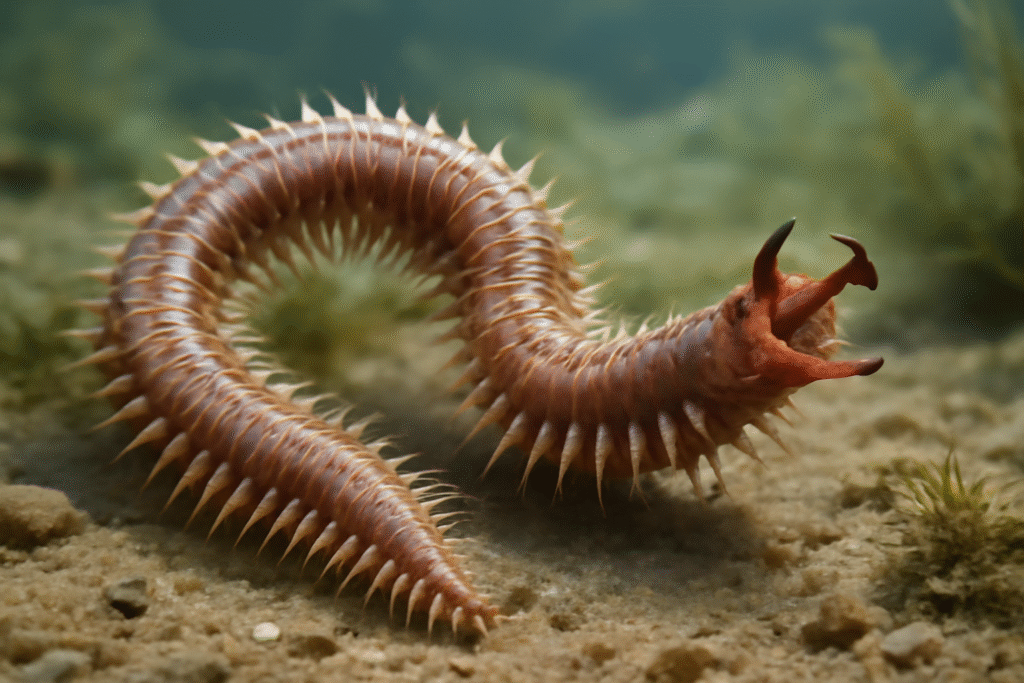
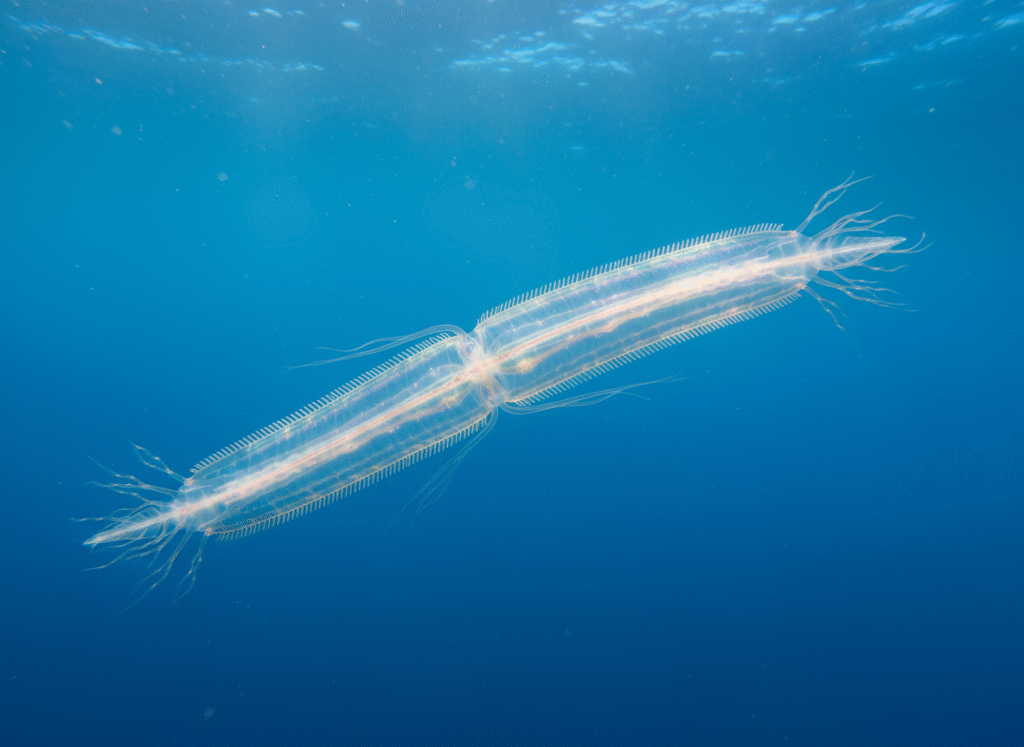
Polynoe
Polynoe: Biology, Classification, Habitat, Anatomy, and Ecological Significance of the Marine Scale Worm Polynoe is a genus of polychaete worms belonging to the family Polynoidae, often collectively known as scale worms due to their distinctive dorsal scales called elytra. These marine annelids inhabit a wide range of oceanic environments from shallow intertidal zones to deep-sea […]