Crayfish vs Lobster : Differences Explained – The fact that lobsters are sometimes referred to as crayfish in some places only serves to further confuse the two species. They do appear strikingly same, so it’s simple to make the mistake. Both have big pincers and robust exoskeletons, and they both live in water. In actuality, however, they belong to two distinct species.
However, how similar are they in reality? First of all, they eat various foods and differ greatly in size. The fact that they reside in entirely different environments—one in the sea, the other in rivers and lakes—may be the most significant distinction between them, though. Come explore all of their distinctions and learn which one resides where.
Understanding both species
Lobsters
Marine crustaceans include lobsters, which belong to the genus Palinurus and family Palinuridae. It is distinguished by its large antennae, strong shell, and elongated body. Its shell is frequently brown to greenish in hue. Typically, the tail is barbed and lengthy. Because of its delicate and mild flavor, its meat is highly prized in the culinary community.
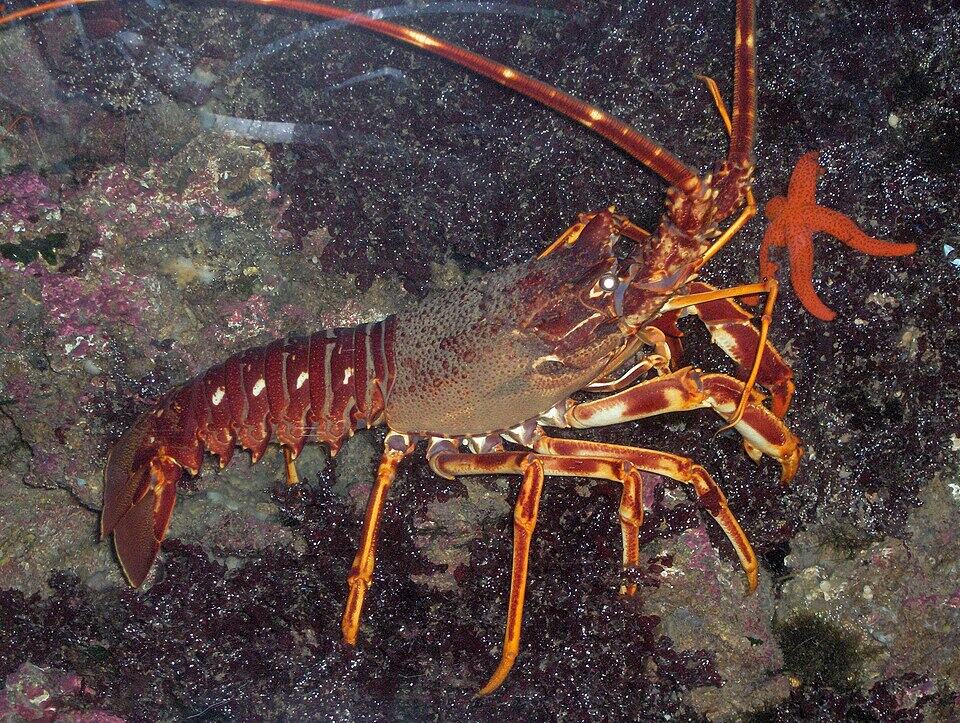

Crayfish
The “Crayfish” is another marine shellfish that is highly prized. Crayfish, also called Homarus americanus, are more frequently found in colder North Atlantic seas, such as the North Sea, than lobster. Its long, sturdy body, hard, blue-green to reddish-brown carapace, and two huge claws—one of which is significantly larger than the other—are what set it apart.
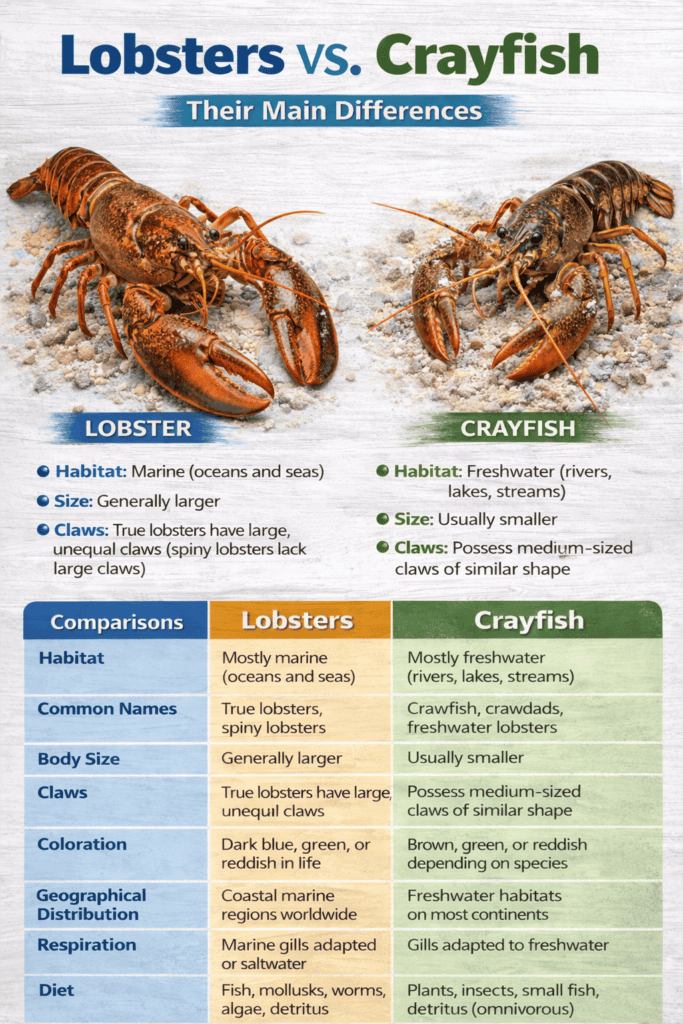
Lobster vs. Crayfish Comparison
Both crayfish and lobsters are invertebrates and crustaceans that frequently lose their hard exoskeleton throughout their lives. They both have ten legs and are decapods. You’re probably asking if there are any distinctions between them at all, given how many things they have in common. Even yet, there are still some significant distinctions between the two, some of which even make it simple to tell them apart.
Their Main Differences Lobsters Vs Crayfish
For a number of reasons, as we previously discussed, people frequently mistake lobsters for crayfish. They may initially appear to be the same animal, however they actually differ from one another due to certain traits. What’s most significant is that crayfish lack claws, but lobsters do.
Here is a clear comparison table showing the main differences between lobsters and crayfish:
| Feature | Lobsters | Crayfish |
| Habitat | Mostly marine (oceans and seas) | Mostly freshwater (rivers, lakes, streams) |
| Common Names | True lobsters, spiny lobsters | Crawfish, crawdads, freshwater lobsters |
| Body Size | Generally larger | Usually smaller |
| Claws | True lobsters have large, unequal claws; spiny lobsters lack large claws | Lacks |
| Coloration | Dark blue, green, or reddish in life | Brown, green, or reddish depending on species |
| Geographical Distribution | Coastal marine regions worldwide | Freshwater habitats on most continents |
| Respiration | Marine gills adapted to saltwater | Gills adapted to freshwater |
| Diet | Fish, mollusks, worms, algae, detritus | Plants, insects, small fish, detritus (omnivorous) |
| Economic Importance | High commercial seafood value | Important in local fisheries and aquaculture |
| Examples | Homarus, Palinurus | Astacus, Procambarus |
Lobster vs. Crayfish: Size
The size of crayfish and lobster is one of their distinctions. Crayfish are 2 to 6 inches long and significantly smaller than lobsters. Larger than other animals, lobsters are usually 8 to 20 inches long, however some can reach several feet.
Lobster vs. Crayfish: Habitat
The simplest method of distinguishing between crayfish and lobsters is to look at their habitats. Lobsters inhabit saltwater in seas and oceans, whereas crayfish inhabit freshwater rivers, lakes, ponds, and streams. Both, however, prefer to hide in cracks and beneath rocks on the muddy bottoms because they are bottom dwellers.
Lobster vs. Crayfish: Color
The colors of crayfish and lobsters appear to be similar at first glance; crayfish are dark blue, green, or black, whilst lobsters are greenish-blue or greenish-brown. On the other hand, lobsters can occasionally be observed in a wide spectrum of vivid hues, such as blue, orange, red, or albino.
Lobster vs. Crayfish: Diet
Despite being omnivores, crayfish and lobsters eat different foods. Small fish, mollusks, snails, clams, some plants, and other small crustaceans are the primary foods consumed by lobsters. Crayfish consume a variety of foods, including dead plants and animals, worms, insects, and plants.
Lobster vs. Crayfish: Lifespan
Additionally, the lifespans of crayfish and lobsters range greatly. The lifespan of crayfish varies from three to eight years, depending on the species. On the other hand, lobsters typically live for 100 years. The oldest lobster ever captured was thought to be 140 years old, and others even far outlive that. Telomerase, an enzyme that repairs DNA, is thought to be the key to their lifespan.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Do crayfish have claws like lobsters?
Yes, crayfish possess a pair of front claws called chelae, similar to those found in true lobsters. - Are crayfish claws the same as lobster claws?
Not exactly. Lobsters usually have two unequal claws—a strong crusher and a sharp cutter—while crayfish claws are generally smaller and more alike in size and shape. - What are crayfish claws used for?
Crayfish use their claws for catching food, defending themselves, digging in the substrate, and interacting with other crayfish. - Do all lobsters have large claws?
No. True lobsters have large claws, but spiny lobsters lack prominent front claws and instead rely on long antennae for defense. - Why are lobster claws stronger than crayfish claws?
Lobsters are typically larger marine animals with specialized claw structures adapted for crushing hard-shelled prey, making their claws more powerful. - Are crayfish and lobsters closely related?
Yes. Both belong to the crustacean order Decapoda, which includes animals with ten legs such as crabs, shrimp, and prawns.
See other Posts also
- Palinurus (crustacean)
- Astacus Astacus
- Palaemon malcolmsonii
- Penaeus (Prawn)
- Squilla (Shrimp)
- PHYLUM ARTHROPODA