Reptile slides of the lizard are widely used in zoology laboratories to study the tissue structure and organ organization of a typical reptile. These slides often include sections of skin, muscle, intestine, liver, kidney, testis, ovary, and scales. Students use lizard slides to understand reptilian adaptations such as keratinized epidermis, well-developed lungs, and efficient circulatory systems. Because lizards represent an important evolutionary step between amphibians and birds, these slides help learners explore vertebrate evolution, organ specialization, and comparative anatomy.
Lizard reptile slides help students study reptilian tissues, scales, and internal organs, offering insight into vertebrate evolution and comparative anatomy.
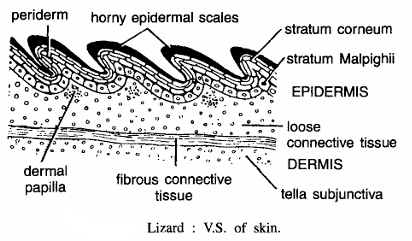
Reptile Slides (Lizard ) V.S. of Skin
Comments
- T.S. skin of lizard shows outer epidermis and inner dermis.
- Epidermis contains horny epidermal scales characteristic of reptilian skin.
- Various layers of epidermis are stratum corneum followed by stratum germinatum or stratum malpighii from which new skin develops.
- Below stratum germinatum in loose connective tissue. Dermal papilla present beneath stratum germinatum.
- Dermis in composed of fibrous connective tissue and conjunctiva tissues.
- Dermis contains muscles, nerves blood vessels and chromatophores.
Identification
Since the section contains epidermal scales and above features, hence it is V.S. skin of lizard.
Reptile Slides (Lizard ) V.S. of Lung
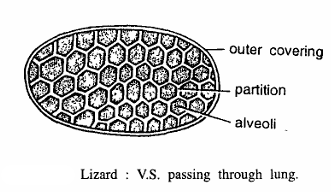
- V.S. lung of lizard shows outer serosa enclosing lung alveoli.
- Inner lining of lung is raised into number of septa like structures, enclosing air sacs or alveoli.
- Lung contains rich blood supply.
- Alveoli are separated by septa.
- Anterior lung is more sacculated thicker and richly vascularised.
- Lung cavity is continuous.
- Bronchus entering into lung does not branches into bronchioles but it directly forms alveoli.
- In lungs deoxygenated blood is brought by pulmonary artery and oxygenated blood carried away by pulmonary vein.
Identification
Since the lung shows alveoli and above features, hence it is V.S. of lung of lizard.
Image References :- Practical zoology Vertebrate